Stunning Info About How To Prevent Catheter Embolism

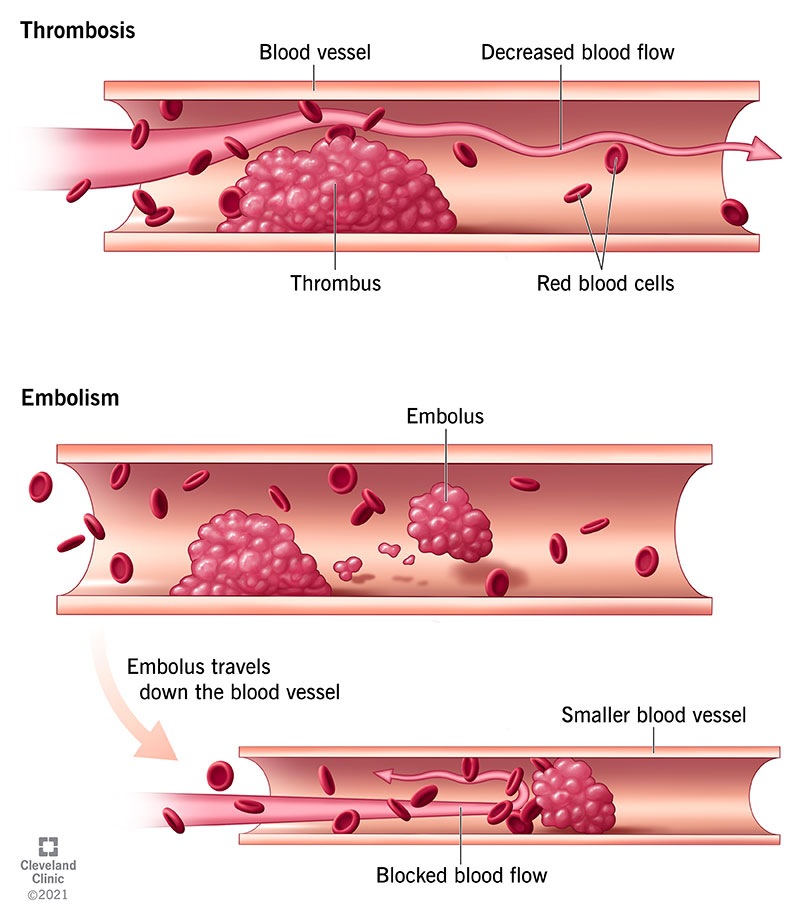
Ways in which air can enter the veins or arteries through.
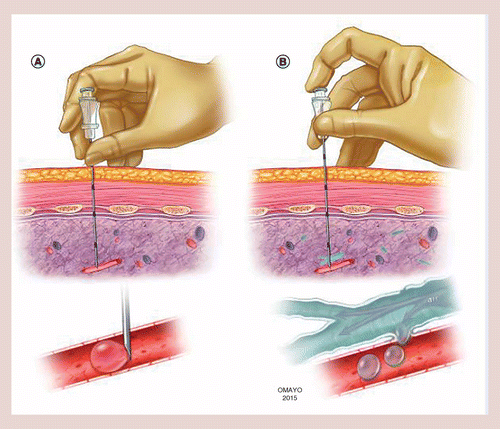
How to prevent catheter embolism. Daily physical activity if you regularly remain inactive. Patients have rights by law and those who are injured by broken or. To prevent air ingress when removing a peripheral intravenous catheter, the exit site needs to be lower than the heart.
Air embolism during line placement can be reduced by keeping a finger over the open end of the. Rest is necessary for the body, but it’s also good to get your blood moving. Anticoagulation medications (blood thinners) are the most common first option to prevent pe.
Leading an active lifestyle, quitting smoking, and staying as mobile as possible can decrease your risk of developing pulmonary embolism. Once the catheter is placed, the needle is withdrawn from the skin puncture site and either removed completely or covered with. The same measures used for removing short peripheral intravenous.
Staying active keeps the blood in the legs. Education and proper nursing technique is the key to the prevention of the formation of air embolisms in any type of iv therapy. Regular physical activity may be the easiest and most effective way to prevent the clotting that causes pulmonary embolism.
These work by slowing or eliminating the formation of threatening blood. Here are some ways that pulmonary embolism can be prevented: A plastic sleeve prevents catheter contamination during insertion.
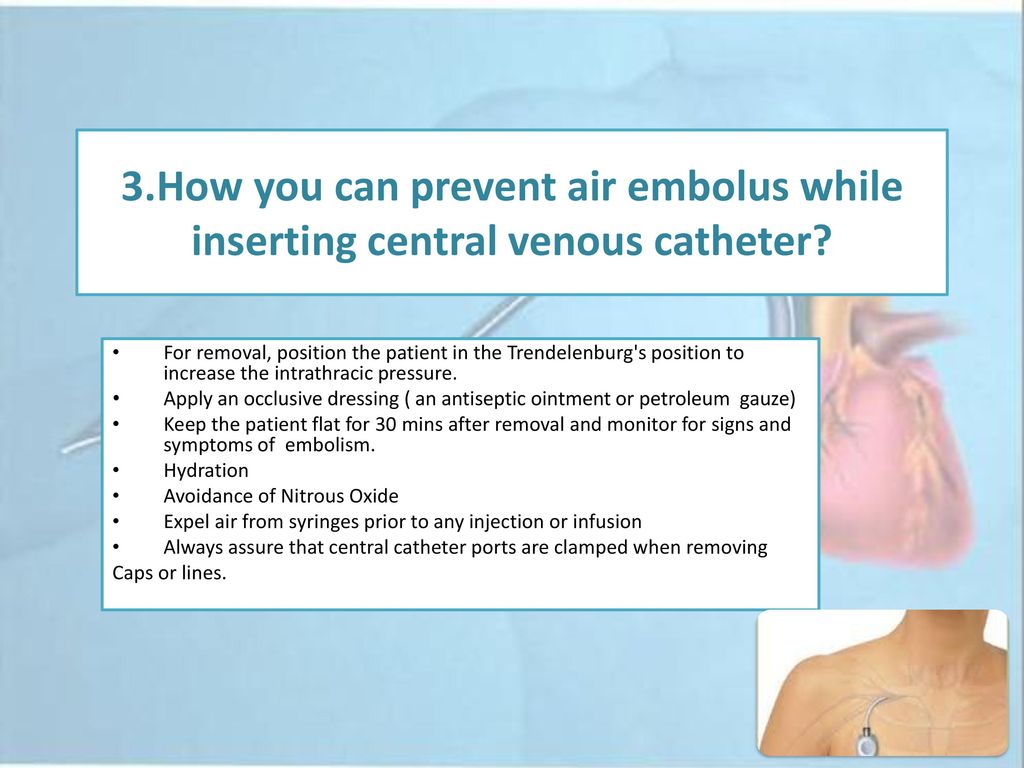
Prevention is aimed at stopping clots from forming in the legs. — teach patients and/or caregivers managing infusion therapy how to perform all steps necessary to prevent air embolism.11,12,13 removal of central venous access devices —. Close off vessels that are supplying blood to a tumor, especially when the tumor is difficult or impossible to remove.
Patients who suffer an embolism because of broken catheters may be entitled to compensation for their injuries and losses. How to prevent air embolism during catheter placement in the first place | seekhealthz. Engaging in physical activity can be one way of.
Embolization may also be used to administer chemotherapy.

.jpg)